Week 1

The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone

Identiyfing sex of the skull
There are few different features that allows us to determine the sex of the skull
Mandible
The mental eminence (chin) is often larger and squarer in males and pointed and smaller in females.

Male Mandible

Female mandible

Male and Female Mandible from above
Forehead
The forehead tends to be more upright in females, while it is often more sloping in males.

Male forehead

Female Forhead
Glabella and supra-orbital ridge
The supra-orbital ridges, sometimes known as the brow ridges and the glabella (approximate centre of the forehead between the supra-orbital ridges) are more pronounced and rounded in males and less marked in females.

male cranium displaying pronounced supra-orbital ridges and glabella

female skull displaying smooth, supra-orbital ridges and glabella
Summary
Male skull
- Larger and heavier skull
- Sloping, less rounded forehead (frontal bone)
- Prominent supraorbital ridge (brow)
- Square chin
- Vertical (acute) angle of the jaw
Female skull
- Smaller and lighter skull
- Rounded forehead (frontal bone)
- Smooth supraorbital ridge (brow)
- Pointed chin
- Sloping (obtuse) angle of the jaw
Week 2
in our second week, we started lecture with looking more into specialistic terminology of skull, and nose. For our exercise during class, we received 2 images that we had to highlight in photoshop. This will let us solidify terminology.




Week 3
Mouth

Philtrum

Philtrum (Lip Crease or ‘Person’s Center’) is a vertical, narrow and long groove that everyone has between the nose and upper lip.
Marionette lines

Marionette lines are wrinkles at the corners of your mouth. These lines are the result of aging and other causes
Nasolabial furrow

The nasolabial folds, commonly known as "smile lines" or "laugh lines".They are the two skin folds that run from each side of the nose to the corners of the mouth
Pillars of the mouth

Mental crease

The chin crease (or 'mental crease') is the horizontal crease that forms between the bottom lip and chin. A deep crease means that there is less support for the lower lip and that the chin can appear to protrude further forward
Mental Proturberance

mental protuberance, the bony prominence at the front of the lower jaw forming the chin.
Orbicularis Oris

orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth. It is a sphincter, or circular muscle, but it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance of circularity.
Teeth

Week 4
Ear

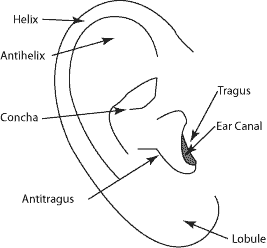
Helix

Helix: The outer rim of the ear that extends from the superior insertion of the ear on the scalp (root) to the termination of the cartilage at the earlobe.
Antihelix

A Y-shaped curved cartilaginous ridge arising from the antitragus and separating the concha, triangular fossa, and scapha. The antihelix represents a folding of the conchal cartilage, and it usually has similar prominence to a well-developed helix.
Tragus

A posterior, slightly inferior, protrusion of skin-covered cartilage, anterior to the auditory meatus. The inferoposterior margin of the tragus forms the anterior wall of the incisura.
Lobe

The soft, fleshy, inferior part of the pinna. It is bounded on its posterosuperior border by the end of the descending helix, on the anterosuperior border by the inferior border of the antitragus and superiorly by the incisura. The earlobe is highly variable in size and in the degree of attachment of the anteroinferior portion to the face.
scaphoid fossa

the depression between the helix and antihelix
Assignment 1




